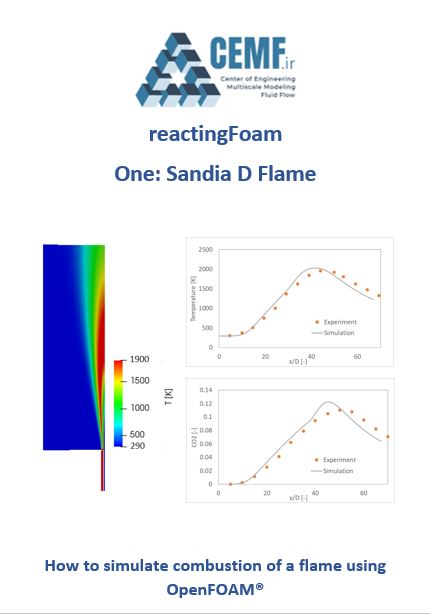
You will learn how to use reactingFOAM solver to simulate a turbulent combustion of methane in air. The simulation is based on the combustion of methane in the Sandia D flame benchmark.
reactingFoam is a transient solver for simulating compressible, laminar/turbulent reactive systems. This solver uses stoichiometry expressions and kinetic data of reactions to obtain consumption and production rate of species. In addition, this solver supports some thermos-physical models to obtain required properties of the fluid mixture phase.
- Solver: reactingFOAM
- Compatible with: OpenFOAM 7, OpenFOAM 6, OpenFOAM v1912
- Model: reactive compressible flow, RAS turbulence model, 3D
- Physical System: Combustion of Methane in the Sandia D flame benchmark.
- Description: Combustion occurs in a lot of equipment in different industries. Therefore, it is vital to be able to model combustion for the design and optimization. One of these equipment is flare that is used most in the energy and petrochemical industries to convert burnable waste gas of the plant into safe and less environmentally-harmful gases.
Here, we simulate the standard Sandia D flame. The flame is composed of two concentric cylinders; the main jet flow exits from the central cylinder and pilot jet exits from the annulus. The main jet is a mixture of Methane and air with a mole proportion 1:3 at 294 K. The pilot jet is the combustion product with the temperature 1880 K. Air flows parallel to the main jet.